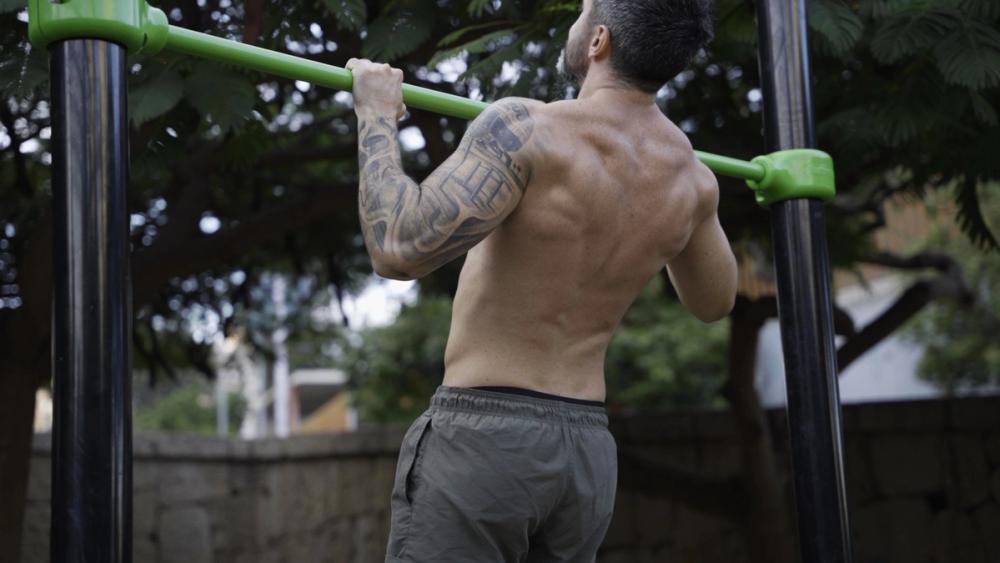

How to achieve your first pull up
Learn how to achieve your first pull-up from scratch with simple progressions, key exercises, common mistakes, and tips to progress faster.

In training terms, a set is a number of repeated movements associated with the contraction and elongation of one or more muscle groups. The number of sets and repetitions changes according to the objectives of each person, but this article will focus on the two most important aspects for who writes, which are hypertrophy and strength.
HYPERTROPHY
If a person trains properly, eats well, and gets enough rest, he is sure to gain muscle mass. If we perform very high series and repetitions (greater than 20) it means that we are not making a great effort so we will not have great results in terms of strength, on the contrary if we perform movements with greater load or greater difficulty our repetitions will decrease (for example, from 20 to 5), but we will have progressed in terms of strength and we will give more growth stimulus to the muscles in terms of one type of fiber.
However, the best way to achieve hypertrophy is to start training with very high loads that allow few repetitions and then work with loads that allow a greater number. That is, start training with high loads that allow performing between 1 to 5 RM (maximum repetitions), in this way the fast or white fibers will be activated to a great extent, and later work with lighter loads that allow performing between 10 to 20 repetitions activating the slow or red fibers in such a way that together we will have achieved a maximum estimate in the muscles, of course it should not be forgotten that a hypercaloric diet will be one of the main factors to take into account whenever you seek to have muscle gains.

STRENGTH
It is related to high loads such as those that allow few repetitions with high loads or in highly complex movements, the latter applies to calisthenics especially in static exercises such as the planche or the front lever. However, Berger cited by Gilles Cometti showed that, in a study carried out on a group of people, which was subjected to tests with loads that allowed 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 12 RM with 95%, 86% , 78%, 70%, 61% and 53% respectively, those who made the most progress in terms of strength were those trained with 4, 6 and 8 RM.
On the other hand, Miguel Vidal Barbier mentions the following ¨The system based on 1RM, will have a set of methods that will fundamentally affect the improvement of maximum dynamic force¨, in other words he tries to tell us that working almost at our 100 % in 1RM will allow us to move a maximum load on a single occasion, fulfilling the entire joint travel, and continuously maintaining a rhythm that allows us to move larger loads over time.
EXERCISES
The exercises that should be used to gain muscle mass, should prioritize the large muscle groups used together. Therefore, exercises such as chin-ups, push-ups, dips, squats, lunges and bridges should not be missing in your routines.
On the other hand, you can use similar versions of these exercises in their easy or difficult way, you can also increase or decrease the difficulty by regulating the weight in each exercise, the important thing is to complete a routine with 6 to 8 exercises that work the same muscle group to that sufficient muscle fatigue can be generated and subsequently its growth.

SETS
In both cases the number of series should be 3 to 4 maximum per exercise, because it is in this number where a faster increase in strength is achieved and by adding more series the technique will be lost in high repetitions such as in the casualties, reducing the correct stimulus and therefore, having mediocre results.
ROUTINES
As mentioned above, in hypertrophy, a work with high loads (or difficult exercises) and low repetitions is needed, along with another that involves lighter loads (or easier exercises) with higher repetitions, this in turn provides us with an improvement in As for strength, resistance and hypertrophy, this will give better efficiency because it will give a better stimulus to the 2 types of muscle fibers (At the end you will find the routines with CALISTENIAPP).
The human body is largely made up of muscle tissue, the function of the muscles is to generate movement through the concentric and eccentric phases. The functional and structural unit of muscles are muscle fibers, which are classified into three types: slow fibers, fast fibers, and intermediate fibers. The function and characteristics of the three types of muscle fibers will be briefly explained below.
Type 1 fibers or slow fibers: also called red fibers due to the content of myoglobin and capillaries, they are the smallest among all types of muscle fibers, they have a large number of mitochondria, thanks to this it is possible to metabolize ATP through oxygen, for this reason it is that red fibers have greater resistance to fatigue and are used to a greater extent in sports of low intensity and long duration (aerobic exercises). Among its main characteristics the following stand out:
Fast type A fibers: also called white fibers, they are large, their activation occurs only when a considerable amount of force is performed (between 1-5 RM), unlike red fibers the number of mitochondria is limited and smaller in size For this reason, its greatest activation occurs in anaerobic sports with heavy loads. Among its main characteristics the following stand out:
Fast fibers type B: Also known as intermediate fibers, with this last name it is understood that they are composed of slow and fast fibers, for which together it is said that they can resist having generating considerable forces, therefore it can be said that there is a transition between slow and fast fibers, although it is largely unknown about the type of training to follow for their activation, they are known to be used in highly explosive events (100m race, 50m swim, etc). Among its main characteristics the following stand out:
Finally, in CALISTENIAPP there are routines specifically to gain muscle mass, which you can see below, and if it is very difficult, you should reduce the repetitions, this in a way that everything said above is applied to optimize results in terms of strength and hypertrophy.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
-- Cometti, G. (2005). Los métodos modernos de musculación (4ª ed). Baladona: Editorial Paidotribo.
-- Vidal, M. (2000). La Fuerza y la musculación en el deporte: Sistemas de entrenamiento con cargas. Madrid: Librerías Deportivas Esteban Sanz.
-- Pearl, B & Moran, G. (2003). La musculación: Preparación para los deportes acondicionamiento general bodybuilding (8ª ed). Barcelona: Editorial Paidotribo.
-- Wilmore, J. & Costill, D. (2007). Fisiologia del esfuerzo y el deporte (6ª ed). Badalona: Editorial Paidotribo.
-- Merí, A. (2005). Fundamentos de la fisiología de la actividad física y el deporte. Madrid: Ed. Médica Panamericana.
-- Billat, V. (2002). Fisiologia y metodología del entrenamiento: de la teoría a la practica. Barcelona: Editorial Paidotribo.
Personalized quiz
Answer 7 quick questions and we will recommend the program that fits you best.

Yerai Alonso
Cofundador de Calisteniapp, referente en calistenia y el street workout en Español. Con más de una década de experiencia, es creador de uno de los canales de YouTube más influyentes del sector. Autor del libro La calle es tu gimnasio, campeón de Canarias y jurado en competiciones nacionales e internacionales.
Join our newsletter
Learn everything you need to know about calisthenics

Learn how to achieve your first pull-up from scratch with simple progressions, key exercises, common mistakes, and tips to progress faster.
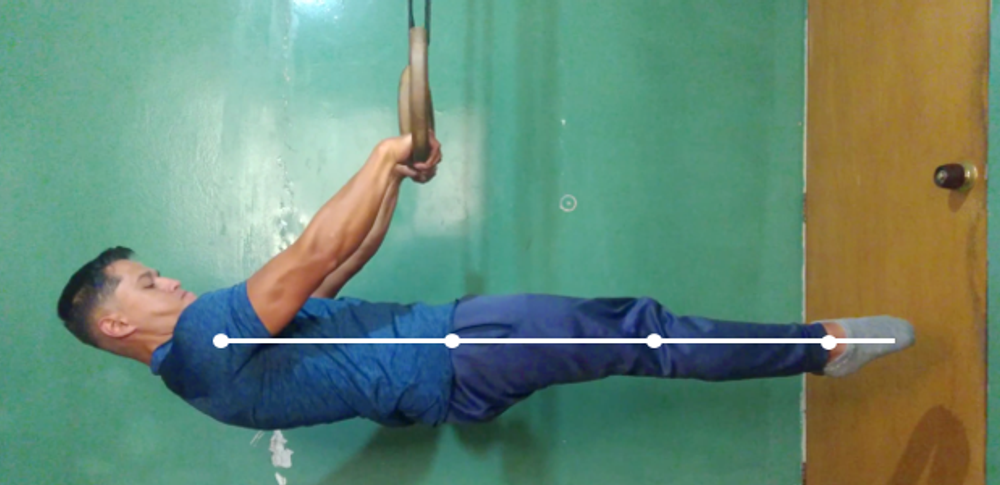

Master the front lever with this step-by-step guide. Learn everything from correct technique and muscles worked to the most effective progressions and key exercises in calisthenics.
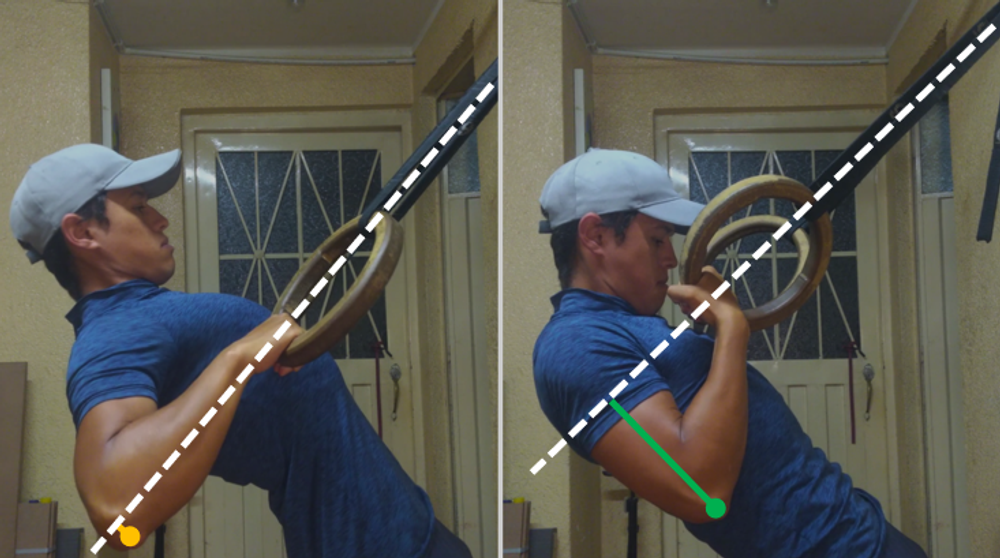

Discover the best calisthenics biceps exercises. Learn how to build arm strength without weights using bodyweight movements, effective progressions, and expert technical tips.
